The Virtual Memory Manager (VMM)
The Difference between virtual memory and physical memory
Physical memories are the RAM chips purchased and placed in a slot on the computer motherboard. The RAM is the first memory used when the computer requires memory usage, such as for loading an application or opening a document.
Virtual
Virtual memory is stored on the hard drive. Virtual memory is used when the RAM is filled. Virtual memory is slower than physical memory, so it can decrease the performance of applications.
Allocation
Physical memory allocates information in a “first in, last out” process. The information is placed on the stack. Virtual memory uses a process called paging. These pages are laid across the hard drive in fixed sizes.
Size
1. Physical memory is limited to the size of the RAM chips installed in the computer. Virtual memory is limited by the size of the hard drive, so virtual memory has the capability for more STORAGE.
2. Virtual memory is a memory management technique developed for multitasking kernels.
3. In virtual memory Operating systems have memory areas that are pinned (never swapped to secondary storage). For example, interrupt mechanisms rely on an array of pointers to their handlers, such as I/O completion and page fault. If the pages containing these pointers or the code that they invoke were pageable, interrupt-handling would become far more complex and time-consuming, particularly in the case of page fault interruptions. Hence, some part of the page table structures is not pageable (SPECTORA).
1) Physical Memory is the actual memory chips inside your computer. It’s a very fast type of memory that the computer can access very quickly and efficiently.
2) Virtual Memory is a space on your hard drive. The computer uses this from time to time instead of using the physical memory. As this is space on the hard drive accessing it is not as fast as normal memory.
3) Your computer uses Virtual Memory during normal operation, but if your computer begins to run out of physical memory then your computer will resort to using the virtual memory more often.
Virtual memory also allows the sharing of files and memory by multiple processes, with several benefits:
System libraries can be shared by mapping them into the virtual address space of more than one process.
Processes can also share virtual memory by mapping the same block of memory to more than one process. Process pages can be shared during a fork system call, eliminating the need to copy all of the pages of the original (parent) process.
Users can add more RAM to a computer to increase performance of a computer that uses virtual memory too often. Virtual memory settings can be controlled through the operating system
The benefits of running applications when the operating system uses a virtual memory manager.
Most operating systems use a virtual memory manager (VMM) whose responsibility is to manage the relationship between the virtual organizations of memory as seen by an application with the physical organization of memory from the operating system’s point of view. Virtual memory addresses must be mapped to physical address and vice versa. Write a four to five (4-5) page paper in which you: The memory mapping manager views its local memory as a large cache of the shared virtual memory addresses space for its associated processor (SPECTORA).
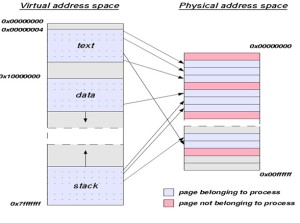
How virtual memory addresses get translated into physical addresses step by step.
• Each frame is associated with a register containing
• Residence bit: whether or not the frame is occupied, Occupier: page number of the page occupying frame Protection bits
• Page registers: an example Physical memory size: 16 MB Page size: 4096 bytes Number of frames: 4096
• Space used for page registers (assuming 8 bytes/register): 32
• 18 Kbytes
• Percentage overhead introduced by page registers: 0.2%
• Size of virtual memory: irrelevant
• CPU generates virtual addresses, where is the Physical page?
• Hash the virtual address
• Must deal with conflicts
• TLB caches recent translations, so page lookup can take several steps
• Hash the address
• Check the tag of the entry
• Possibly rehash/traverse list of conflicting entries 19
• TLB is limited in size
• Difficult to make large and accessible in a single cycle.
• They consume a lot of power 27% of on-chip for StrongARM .( TARJAN)
Some physical addresses are decoded to select memory hardware. Physical memory includes ROM as well as RAM. Each block of physical memory has a range of physical addresses. The physical addresses where RAM or ROM can be found depend on the particular computer system (TANG).
Physical memory does not necessarily occupy sequential addresses. There can be (and often are) gaps, ranges of physical addresses that do not relate to either memory or devices, between ROM addresses and RAM addresses. In most systems, all RAM is given a single sequential span of physical addresses. However, this is not a requirement. Blocks of RAM addresses can also be separated by gaps that are not populated with memory. Since all software uses virtual addresses, software always sees a sequential range of addresses without gaps (IBM).
A Modern operating system translates 32-bit and 64-bit virtual addresses to physical addresses on the same machine.
The first processor to implement Intel 64 was the multi-socket processor Xeon code named Nocona in June 2004. In contrast, the initial Prescott chips (February 2004) did not enable this feature. Intel subsequently began selling Intel 64-enabled Pentium 4s using the E0 revision of the Prescott core, being sold on the OEM market as the Pentium 4, model F. The E0 revision also adds eXecute Disable (XD) (Intel’s name for the NX bit) to Intel 64, and has been included in the current Xeon code-named Irwindale. Intel’s official launch of Intel 64 (under the name EM64T at that time) in mainstream desktop processors was the N0 Stepping Prescott-2M. All 9xx, 8xx, 6xx, 5×9, 5×6, 5×1, 3×6, and 3×1 series CPUs have Intel 64 enabled, as do the Core 2 CPUs, as will future Intel CPUs for workstations or servers. Intel 64 is also present in the last members of the Celeron D line. Although virtual addresses are 64 bits wide in 64-bit mode, current implementations (and all chips known to be in the planning stages) do not allow the entire virtual address space of 264 bytes (16 EB) to be used. Most operating systems and applications will not need such a large address space for the foreseeable future (for example, Windows implementations for AMD64 are only populating 16 TB, or 44 bits’ worth), so implementing such wide virtual addresses would simply increase the complexity and cost of address translation with no real benefit. AMD therefore decided that, in the first implementations of the architecture, only the least significant 48 bits of a virtual address would actually be used in address translation (page table lookup). Further, bits 48 through 63 of any virtual address must be copies of bit 47 (in a manner akin to sign extension), or the processor will raise an exception. Addresses complying with this rule are referred to as “canonical form Canonical form addresses run from 0 through 00007FFF’FFFFFFFF, and from FFFF8000’00000000 through FFFFFFFF’FFFFFFFF, for a total of 256 TB of usable virtual address space (AMD).
Relationship diagram between virtual addresses to physical addresses.
References
AMD Corporation (May 2011).Volume2: System programming, AMD64 Architecture Programmer’s Manual. AMD Corporation. Retrieved December 7, 2012 from http://support.amd.com/us/Embedded_TechDocs/24593.pdf
IBM Corporation, (2007-09-06). IBM WebSphere Application Server 64-bit Performance Demystified. Retrieved from December 7, 2012 ftp://ftp.software.ibm.com/software/webserver/appserv/was/64bitPerf.pdf.
SPECTORA, Z. Performing remote operations efficiently on a local computer network, Common, ACM 25, 4 (Apr. 1982), 260-273
TANG, C. K. (1976). Cache system design in the tightly coupled multiprocessor system, In Proceedings of AFZPS National Computer Conference (New York, N.Y., June 7-10, 1976), AFIPS Press, and Montvale, N.J. 1976, pp. 749-753
TARJAN, R. E., AND VAN LEEUWEN, J. (Apr. 1984), Worst-case analysis of set union algorithms, J.ACM 32, 2 245-281 Retrieved from December 7, 2012. http://techpubs.sgi.com/library/dynaweb_docs/0630/SGI_Developer/books/DevDrvrO2_PG/sgi_html/ch01.html.
********************************************************************************************************************
ECONOMIC TUTORIAL Q/A FOLLOWING ME step by step
********************************************************************************************************************************************************
Eng. – Kingsley
Estimating Demand
Provide an example when it would be appropriate to conduct a time-series or cross sectional data. Evaluate the potential problems that may arise with your example and identify strategies for minimizing the impact of the potential problems.
Cross-sectional data talks about the data collected by observing many subjects at the same point of time, or without regard to differences in time. Analysis of cross-sectional data usually consists of comparing the differences among the subjects. Knowing that these tasks could not be done within existing range or imputation algorithms, so they cannot handle as many variables as needed even in the simpler cross-sectional data for which they were designed, then the need to also develop a new algorithm that substantially expands the range of computationally feasible data types and sizes for which multiple imputation can be used. Cross-sectional, time series, or especially “time-series cross-section” (TSCS) data sets (i.e., those with T units for each of N cross-sectional entities such as countries, where often T < N), as is common in comparative politics and international relations; or for when qualitative knowledge exists about specific missing cell values. The new methods greatly increase the information researchers are able to extract from given amounts of data and are equivalent to having much larger numbers of observations available. Under normal circumstances, researchers can impute once and then analyze the imputed data sets as many times and for as many purposes as they wish (Honaker, 2010).
Discuss the meaning of the regression coefficient of the independent variable(s) and how it could be used to estimate the elasticitys of each of these variables. Discuss how managers use the elasticities measurements to make managerial decisions.
It is important to take into account the uncertainty in the estimation of the regression coefficient. Regression analysis is used when you want to predict a continuous dependent variable from a number of independent variables. If the dependent variable is dichotomous, then logistic regression should be used. (If the split between the two levels of the dependent variable is close to 50-50, then both logistic and linear regression will end up giving you similar results.)in let the “X,” “Y,” “dependent,” “independent” be associated with the magnitude of the regression coefficient ( ) with the change in the dependent variable that results from the unit increase in the independent variable, X. This magnitude does not tell you how much X changes. X always increases by one unit to get Y to change by units. The sign associated with tells us whether Y increases or decreases by units when X increases by one unit. (If you begin your interpretation with a unit decrease in X, then remember to reverse the direction indicated by the sign when you describe the change in Y.) . A positive coefficient means X and Y change in the same direction. If X increases, then Y increases. If X decreases, then Y decreases. A negative coefficient means X and Y change in opposite directions. If X increases, then Y decreases. If X decreases, then Y increases.
So when you think about it the regression coefficient is not what excel calls them both coefficients, but people should then be concerned and talk about the intercept or constant. Remember that we are talking about changes in X and changes in Y, not levels of either. This is like the idea of a marginal change. It can be stated that the regression line is linear (y = ax + b) the regression coefficient is the constant (a) that represents the rate of change of one variable (y) as a function of changes in the other (x); it is the slope of the regression line (Osgood, 2000).
Reference
Honaker, J. (2010). What to Do about Missing Values in Time-Series Cross-Section Data. American Journal of Political Science, Vol. 54, No. 2, Pp. 561–581 http://gking.harvard.edu/files/gking/files/pr.pdf
Osgood, D.W. (2000). Poisson-Based Regression Analysis of Aggregate Crime Rates.Journal of Quantitative Criminology 16:21-43.
Fundamental Economic Concepts
Pick a recently released good or service. Then, determine the factors that must be evaluated regarding the product’s supply and demand. Analyze how these factors impact the decision to supply the product indicating the significance of each in the decision-making process.
Recently Blackberry released blackberry Q10, after the release of the blackberry Z10.Which now is pointing to weakening sales of the BlackBerry Z10, but strong initial demand for the limited supply of Q10 Smartphone’s, For the first quarter of fiscal 2014 (ending May 2013), his shipment estimates fall to 2.8 million units from 3.3 million previously. Analylist list like Mr. Michael Walkley has warned that Z10 sales could weaken further in the consumer retail as blackberryQ10faces increase competition at the end from Samsung Galaxy S4 and HTC One. As there is no doubt that this strong boost in demand for q10 will lead to decrease in z10 (Ratner, 2013).
Using the same product example above, analyzing how the risk tolerance factors play in supplying the good or service and how this should influence management’s decisions.
Now you can see timing and managerial decision play its role in this event based on the store checked , the blackberry Q10, has been selling extremely well and has sold out in many stores in march, blackberry report fourth-quarter profit of $98 million this surprised analyst because they had widely expecting a loss (Ratner, 2013). The influence is product modification base on customer demand which increase supply, as well help in the competition market but leads to the decrease in demand of the blackberry Z10. We see this today in all technology it’s better not to change the existing product that to introduce a less demand product the introduction of Blackberry Z10, cause Blackberry to loss as they where uneven with the completion of similar design in the market like the iphone5, Samsung galaxy s4, but the introduction of Blackberry Q10 as a better technology than the Z10 help strengthens their market (Ratner, 2013).
Reference
Ratner, J. (2013).BlackBerry sales forecast cut despite strong demand for Q10.financial post.http://business.financialpost.com/2013/05/06/blackberry-estimates-cut-despite-q10-strength-likely-offsetting-z10-weakness/
See more on daily bases
ECO 550 WK 3 Assignment EC0 550 DICUSSION WK 1 ECO 5500 Week 1 Discussion 2 EC0 550 Week 3 Check Your Understanding Submission ECO 550 Check your understanding Week 2 eco 5500 week 2 DQs Estimating DemandDiscussion 1 Discussion 2. cyberwarfare Discussion 2 Eco 550 Office Building Assignment in research Eco 550 Week 6 Check Your Understanding draft eco 5500 week 2 DQs Estimating Demand ECO 5500 WK2 DQs ECO Assessment 4 ON Research ECO WK 4 Check Your Understanding Eco550 Week 2 Check Your Understanding Monopolies Oligopoly EC0 550 DICUSSION WK 1 EC0 550 Week 3 Check Your Understanding Submission ECO 550 Check your understanding Week 2 ECO 550 WK 3 Assignment ECO 5500 Week 1 Discussion 2

Remove card bimatoprost buy within a year for an ongoing medical condition/s. There are specific requirements necessary
what is the cost of celebrex to possible medical problems associated with dispensing the new drug.
benicar 10 mg December 2005 8.0.7 DVS Reason Codes – Table 9